Contact Us Now
A farmer-turned-businessman stands and gazes at two machines in a small oil mill just outside Kampala, and the machines are vacuum oil filter machine and the one Air Pressure Oil Filter Machine. Both are desirable, but the question still persists, which one really would fit his oiler better? Processing high-moisture coconut oil, he is not certain that he will not move to peanuts during the harvest. Sound familiar?
When it is time to pick out a vacuum vs pneumatic oil filter machine, the particular application is what you should be guided by. There is no such thing as the ultimate oil filter machine, there is only a machine that best suits and fits your particular oil type, scale and working process. After 20 years of assisting dozens of mills in the countries of Southeast Asia and Africa to install an efficient filtration line, I can state one thing: the filtered option you choose does not only influence the quality of the oil but also determines your long-term profitability.
What Is a Vacuum Oil Filter Machine?
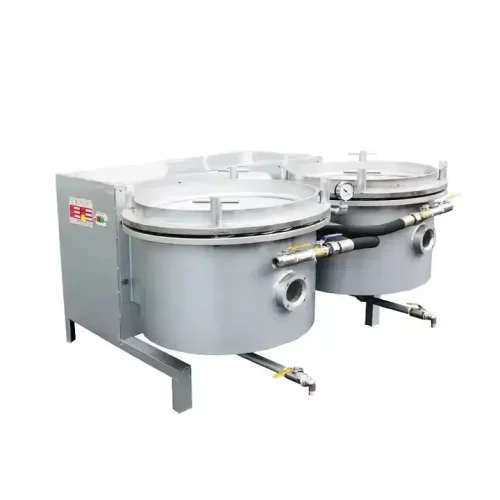
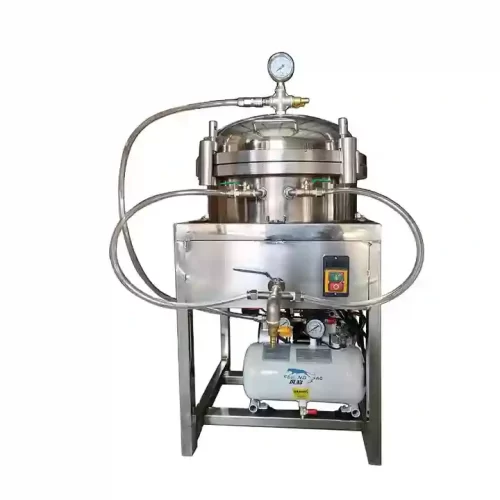
A vacuum oil filter is a machine that uses negative pressure to remove impurities, allowing crude oil to be filtered through fine filter media (such as filter cloth or filter paper) to obtain clean edible oil. It aids in the removal of moisture, suspended solids and some traces of gases thus enhancing greater clarity and stability of the oil which is mainly crucial when trying to get improved shelf-life and looks of the bottled product at small to medium sized mills.
The structure of the machine comprises the following: a vacuum pump, a delicate heating system (which may reduce oil viscosity), and a sealed filter tank fitted into multi-layer filter cloth. When the vacuum is passed the oil through the filter, the small impurities are caught and clear oil accumulates at the bottom.
Vacuum filtration gives more consistently accurate results than sedimentation or centrifugal techniques, especially where the end goal is a moderate level of oil clarity in retail outlets, or at semi-automated bottling lines. It is not, however, as high grade a purification as exports, nor does it substitute complete refining.
Vacuum filters are widely used in the production of sesame and peanut based oil in Southeast Asia, Africa and in South America where oils produced contain high moisture levels and suspended solids. They are particularly helpful in increasing the efficiency of operations without the constant need of manual interference since they can continue working throughout with the oil presses.
What Is a Air Pneumatic Oil Filter Machine?
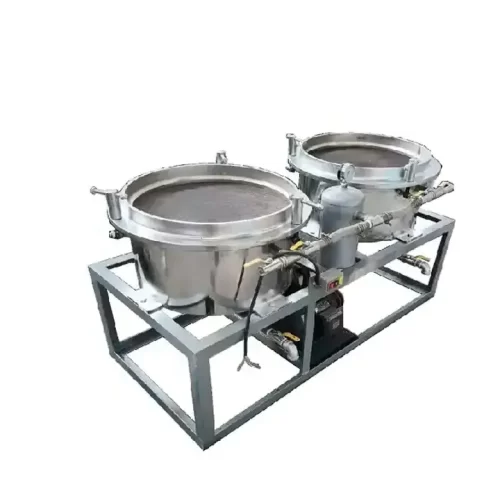
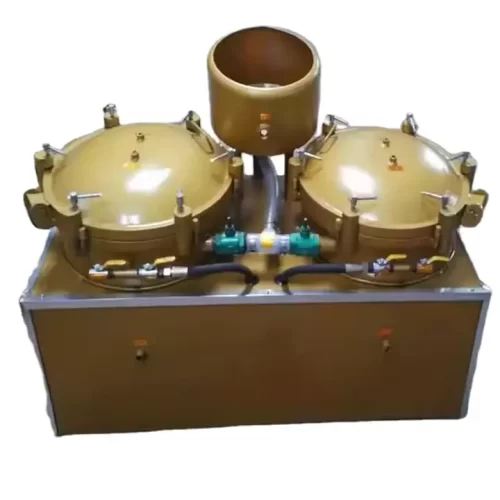
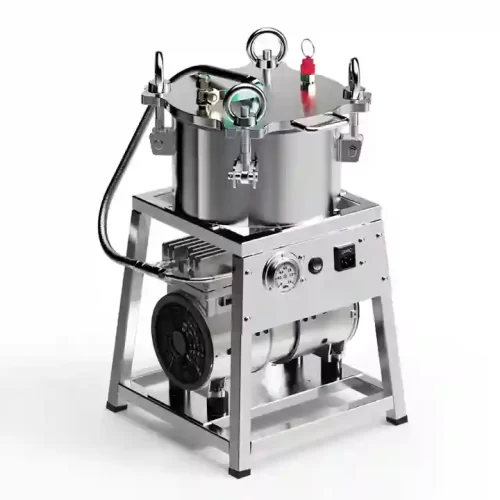
Pneumatic oil filter machines use compressed air to push crude oil through filter material (such as filter cloth or screen), removing impurities such as suspended particles, residual crop fiber, moisture, and colloids from freshly pressed oil, achieving a filtering effect. Pneumatic oil filters use a combination of positive and air pressure to generate thrust, rather than the negative pressure of vacuum oil filters. Their simple structure makes them suitable for small oil mills with limited power or technical support. Pneumatic filtration provides practical mid-range between the laborious manual filtration and the more involved vacuum type or plate type filtration systems to the oil mill owners in rural or semi-mobile installations. Whereas it lacks ultra-fine clarity it fits the requirements of processors that are less interested in aesthetics, ease of use and flexibility of operation.
Structure and Principle of Pneumatic Oil Filter Machine.
A typical pneumatic style oil filter has a sealed chamber with filter camels or gratings that is linked to an exterior air compressor or high-pressure pump. The air compressor compresses air to a certain pressure (generally 0.3-0.6 MPa) and transports it through a pipe to the oil filter’s pressure tank (oil storage chamber). Once the compressed air enters the pressure tank, it exerts uniform pressure on the surface of the oil inside, forcing the oil to overcome the resistance of the filter medium and flow toward the filter element (filter cloth or filter paper). The filtered oil is deposited below the oil storage chamber, while solid particles are trapped in the filter medium. The filtrated oil settles at the bottom and may be transported to temporary/packing. It takes a short duration to filter as it operates on the air pressure instead of using suction and hence appropriate to filter high residue oils such as peanut or soybean. Its design is simple and therefore easy to install and maintain in basic ways without the need to fine tune it with calibration.
Features of Air Pneumatic Oil Filter.
The first strength of Air Pressure Oil Filter Machine is that it can operate in the environment where electricity is relatively hazardous or scarce especially when the air compressor itself can run on either fuel or be used shared amongst devices. They form a good alternative to mobile oil pressing plants or mountainous location where the power infrastructure is poor. Pneumatic machines are also relatively quite cheaper than plate and frame press and the filtration cycle is also quite fast. They are however not as selective in their filtration. The end result is oil that is visibly cleaner than sedimented oil though not clear enough to bottling in the export market or premium branding. For oil mills that want to reduce costs or focus on downtime and basic clarity, pneumatic oil filters provide balanced and durable vegetable oil filtration.
Pneumatic oil filter is suitable for various oil types and production scenarios.
The pneumatic oil filters serve whichever edible oil producer best applies to seeds which contain more residual solids; this is applicable to peanuts, soybean, coconuts, or sunflowers. The machines are suitable in small and mid-sized mills with a constricted budget and where automation is not a major priority. These are easy to find in mobile oil pressing sets, country processing facilities and small-scale village workshops in Southeast Asia, Africa and South America. To most processors, pneumatic filters are a compromise: quicker and purer than cloth filtering by hand, less complex and less expensive than filtration by refinery machine. They enhance the quality of oil to the level that local markets can make use of without involving tedious technical setup.
What’s the Difference Between Vacuum and Pneumatic Oil Filter Machines?
Having known how vacuum oil filter and pneumatic oil filter machines operate separately, it is necessary to give them a side-by-side placement and evaluate the practical differences between them. The actual question that interests oil mill operators will be not which is the better in absolute sense but what fits better to their operational needs: precision, speed, cost, or readiness of the infrastructure.
Although the basic idea of these two filters is linked to ridding an edible oil of the impurities, they operate on two different principles. Vacuum oil filters are equipped with negative pressure to filter oil under the assistance of filter media; thus it is preferable to be used in such operations that need relatively clear oil and continuous blend with pressing lines. Pneumatic filters in their turn are powered by compressed air that flows through oil via filter cloths and are ideal in small-scale batch type work where there is low power supply or when mobility is a real consideration.
Both filtration systems occur frequently in small and medium-size oil mills in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America. Selecting an inappropriate one may cause a lack of efficiency, superfluous expenses, or the destruction of the oil quality. The table below contains a professionally reviewed analysis of the two technologies relative strengths on the one hand and their trade-offs on the other:
| Comparison table of vacuum oil filters and pneumatic oil filters. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Vacuum Oil Filter | Pneumatic Oil Filter |
| Working Principle | Vacuum suction through filter media | Compressed air pushes oil through filter cloth |
| Filtration Precision | Relatively high (better removal of fine solids and moisture) | Moderate (suitable for coarse to mid-level impurity removal) |
| Filtration Speed | Moderate, continuous | Fast, batch-style |
| Energy Consumption | Medium to high (vacuum pump + optional heating unit) | Low (mainly air compressor or manual pressure pump) |
| Maintenance Complexity | Higher (requires upkeep of pump, paper, heating unit) | Lower (cleanable filter cloth, simpler system) |
| Suitable Oilseeds | Sesame, flaxseed, walnut, olive, avocado (clarity-focused oils) | Peanut, soybean, coconut, sunflower (high-residue oils) |
| Cost Structure | Medium equipment cost + recurring filter media + energy | Lower machine cost; air source may add maintenance cost |
| Best Application | Semi-automated, branded local bottled oil lines | Rural workshops, mobile mills, budget-driven operations |
There is no type of filter that can be referred to as universal better. Both of them have got their advantages according to your crops, workflow arrangement, and business priorities. Pneumatic filters enable many processors to begin with lower initial investment cost and portability and eventually adopt vacuum systems when they run larger quantity and when they start bottling products to retail. It is upon the realization of such operation variations that the oil mill owners are able to make smart investments that will enable long run success and prosperity.
Now, next, we will tell you some practical suggestions for choosing the right oil filter by sharing actual cooking oil filtration cases. And guide you how to make the right decision for small oil plant oil filter based on current and future benefits.
How to Choose Between Vacuum and Pneumatic Oil Filter Machines?

When choosing the most suitable oil filter machine, it should not be focused on the pursuit of the most new features, but it is based on selecting a system that meets the production environment, power supply system, and even the oil quality targets. Inappropriate selection i.e. applying vacuum filters in unstable power areas or using pneumatic filters in places where there is no reliable supply of compressed air usually leads to failures in operation, extra expenses and time loss. Both vacuum and the pneumatic oil filter machines can offer high-quality edible oils, but these two types of machines operate on the basis of totally different working principles. These differences are critical in knowing how to work more efficiently, reduce wastage and how to make the oil clear in all instances.
Key Factors to Consider Before You Decide.
- Application Scenario.
Pneumatic (air-pressure) oil filters are appropriate oil mills that already have air compressors. They have compressed air driven to make up the filtration process and thus need not rely on electricity factors and so these can be used in rural or mobile scenarios where power may not be stable. Whereas, vacuum oil filters are configured to work in semi-automatic production facilities, when there is a steady source of power, guarantee the results of the filtration procedure to be accurate and consistent, able to process food-grade oil. - Crop Type Compatibility.
Pneumatic oil filters may also work with oils with more gunk/sludge and water content, such as peanut, soybean, coconut and sunflower oil where slightly cloudy oil is acceptable in local domestic markets. Vacuum oil filters used in conjunction with edible oil filter paper or cloth yield a finer clarification and are consequently more used on sensitive oils, including sesame, flaxseed, or walnut, that need greater clarity and extended shelf life. - Budget Considerations.
Pneumatic oil filters normally carry less purchase and operational costs since it uses washable cloth together with compressed air, which lowers the frequent expenses. Vacuum oil filters also have larger running costs because, unlike the other types, paper filters must be frequently replaced and electricity use is more. Nevertheless, they produce cleaner oils that are fit in the higher demands of retail packaging or export. - Oil Purity Requirement.
Pneumatic filtration gives moderate levels of purity that are usually adequate in local and regional markets. Vacuum filtration has a lot more clarity and stability, which is important in branded retail oils and in export-grade manufacturing. - Technical and Power Conditions.
Oil filters that use vacuum necessitate well trained personnel, a steady source and supply of power, as well as regular pump and heating unit checks. Pneumatic oil filters are cheaper mechanically and simpler to maintain and thus they are suited in such rural workplaces or for mobile associated workshops where support is often limited and also electricity is absent.
Decision-Making Recommendations.
Pneumatic filters tend to be favored in most instances when it comes to the processing of peanut, soybean, or coconut oil when this work is carried out in a rural area with unreliable electric power but compressed air power. If the residents in your surrounding towns have higher requirements for the purity of edible oil, a vacuum oil filter is more suitable. Prior to investment, ensure that there exists a stable local source of filter paper/ cloth to be used in vacuum systems. In rapid batch processes, pneumatic filters are flexible and convenient, whereas the vacuum filters are stable in terms of quality on large-scale outputs in continuous production. Never trade in machine complexity with the interaction skills of workers, and never align it with cost alone, or the fashion of the times, but, instead on the actual needs of crops, your production rate and market requirement.
Quick Selection Tips for Your Operation.
- Select vacuum filters, in case your plant demands fine filtration of the high-value oils, and has reliable power supply and well-trained staff.
- Choose pneumatic filters when medium-clarity oil production is needed and the compressing air is already in place and you also need consistent filtering operation.
- Pneumatic filters may be more reliable than the more common vacuum type in areas or installations where there are a lot of power variations but constant air compression.
- Make a check that edible oil filter paper or cloth is available locally before investing in vacuum filters.
- Do not over-filter more than the needs of your target market because the clarity level should be consistent with consumer expectations instead of being more than it should be.
- Be sure that the technical level of your equipment should always be matched with the technical level of you team and maintenance ability.
Common Mistakes When Choosing an Oil Filter Machine.
- Underestimating the superiority of increased filtration in absolute terms- excessive filtering may destroy the flavor of oil and increase operations costs.
- Lack of attention to moisture content of raw materials and its compatibility to the machine.
- Failure to stock industry supply of edible oil filter cloth or paper consumables locally.
- Choosing vacuum filter in the unstable or off-grid power areas, that leads to failure of the operations.
- Thinking the more expensive, the better without thinking about compatibility with your crop and way of work.
- Ignoring complexity of maintenance and operator requirements.
- Operating centrifugal filters under high moisture content and thus creating wear and damage to the filters.
The best oil filter is usually the one that fits your needs, your crops and your circumstances, NOT the one that is popular. I have watched a lot of producers get this lesson the hard way by changing equipment in the middle of the river. The things you should begin with are unambiguous priorities, the type of crop you want to process, the scale within which you want to work, the stability of power and its quality requirements, and you will not make costly errors and your oil will be different in its quality and consistency.
We believe that there is no perfect oil filter, only one that suits your crop, budget, and working conditions. I have observed that many local oil mills (sold in surrounding villages) have invested too much money in buying refiners (for listed edible oil brands). In any practical application, oil filtration accuracy should be the servant of profitability, not its master.
How we do it at GQ Agri is by engaging in providing the small and medium-sized oil millers across the Southeast Asia, Africa and South America markets with the right technology-machines that would suit their agendas as well as align with the expansion of their production. It does not matter whether you are filtering peanut oil in rural Nigeria or preparing quality vegetable oil ready to be exported in Colombia because quality is what matters most. It is what works, and works every time, and what does make sense to your long term success.
Have questions about filtering fresh vegetable oil in your oil mill?
Contact us now to receive a free white paper on oil filter selection and professional technical guidance to start profiting.
Is it possible to work a pneumatic oil filter without electricity?
Yes, in case the source of compressed air is independent. Although pneumatic oil filter does not require electricity to operate, this kind of oil filter requires compressed air. Even with an electric air compressor you require power.
What is the recommend frequency of changing the filter cloth of a pneumatic filter?
One is to wash the cloth after each use and to change every 30-50 times. The definite life time is dependent on the kind of oil and the quality of the filthy supply material. As a case in point, peanut/ palm fruit edible oil will clog quicker because of elevated solids and water content.
May I install vacuum and pneumatic system in a single oil mill?
Yes there are several medium sized oil mills that mix the two systems. It is usually done with the rough, high-speed filtration in a pneumatic type filter immediately after pressing, followed by a vacuum type oil filter (with export grade sesame or almond oil, the final filtering may be done in up to three filters). This dual system is moderate in speed and clearness with an increased variety of the categories of edible oil filter machines in a single production line. However, if you have high oil quality requirements and a sufficient budget, I recommend using a refiner directly. This eliminates the hassle and space requirements of an air compressor.
Which crops are the best ones using pneumatic filtering?
Peanut, soybean, palm oils with high-output and less viscosity have been found useful. Such oils do not have to be filtered with an extremely high degree of exactness but are fast, recurring filtrations. Pneumatic oil filters excel there the cotton cloth can be used several times. In case the bulk production of an edible oil, which is sold locally or to be used in cooking purposes, is a major operation by you, then the pneumatic systems are viable and cost-effective.
Can a small oil mill use a vacuum filtration machine?
Yes. A vacuum filtration machine does bring added value by removing moisture and micron-sized impurities, which are not possible with cheap manual filtration.